IABP
title: Intra Aortic Balloon Pump tags: #FFICM #cardiac #mechanical_cardiac_support notebook: ð-FFICM type: anki
- [[mechanical_circulatory_support]]
- [[Acute Heart Failure]]
category:
This is a "counterpulsation pump" in the descending aorta. It's the most common assist device. 1
| Flashcard | type:basic |
|---|---|
| What type of pump is an Intra Aortic Baloon Pump | A "counterpulsation" pump |
| Flashcard | type:cloze |
|---|---|
| An {{c3::IABP::device}} {{c1::inflates}} at {{c2::the start of diastole::cardiac cycle}} and {{c1::deflates}} {{c2::just before systole::cardiac cycle}} | |
| {{c1::Inflation}} of an IABP is triggered by {{c2::the onset of diastole::cardiac cycle}}, which on ECG is {{c3::the middle of the T wave::ECG point}} and on arterial line is {{c4::the dicrotic notch::arterial waveform}} | |
| {{c1::Deflation}} of an IABP is triggered by {{c2:: just before the start of systole::cardiac cycle}}, which on ECG is {{c3:: the peak of the R wave::ECG point}}, and on arterial line is {{c1::just before the main upstroke::arterial waveform}} | |
| On arterial waveform, balloon {{c1::inflation}} creates a {{c2::Deep V in dicrotic notch}} | |
| On arterial waveform, balloon {{c1::deflation}} creates a {{c2::second peak in waveform}} |
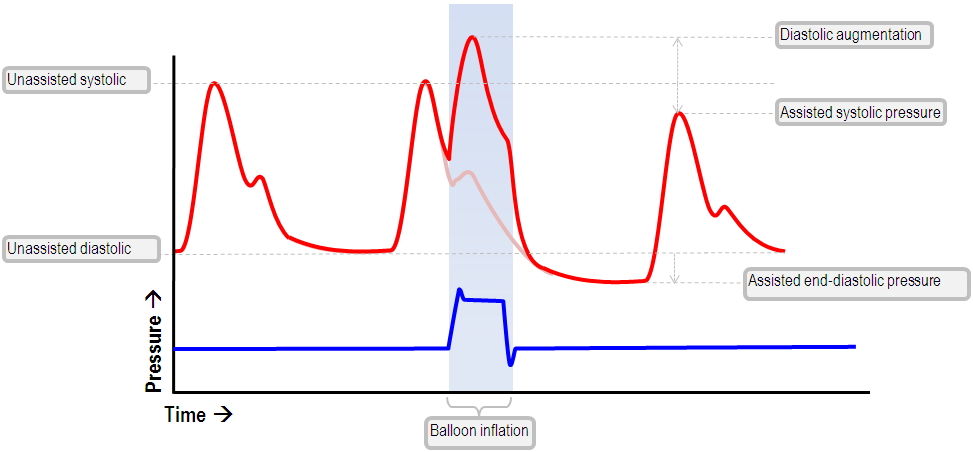
- The balloon inflates at the onset of diastole, and deflates just before systole. 3
- Inflation is triggered by ECG middle of T wave, as that is onset of diastole. And by Art Line through Dicrotic Notch, as that is after closure of aortic valve. 3
- Deflation is triggered by ECG peak of R wave, as that is onset of systole. And by Art Line through just before upstroke of waveform, as that is aortic valve opening. 3
So balloon inflation creates a deep V in dicrotic notch on waveform. Deflation creates a second peak in waveform. 3
Because trigger is by ECG, arrythmias and interferences cause balloon problems. 3
| Flashcard | type:basic |
|---|---|
| Why do arrhythmias mess up your IABP? | Because it needs an ECG to trigger inflation and deflation? |
| Why does tachycardia mess up your IABP? | Because it needs a nice long diastolic time for coronary artery perfusion |
Inflating in diastole pushes some blood forward into the aorta, and some blood backwards, into the coronary arteries. 3
This blood pushed forward, initially the pressure of it just stretches the aortic root outwards a bit, and then that recoils and pushes the blood properly forward. This stretch and recoil is called the "Windkessel effect". 3
The aims of a balloon pump (also basically the aims of cardiac intensive care):
The effect of the balloon pump depends on:
- The volume of the balloon - Bigger balloon = Bigger effects 3
- HR - Slower HR = More Diastolic Time = More Time for Balloon Augmentation 3
- Aortic Compliance = Stretchier Aorta/Decreased SVR = Less pressure for balloon to push blood backwards with = Less diastolic augmentation 3
The effect of the balloon pump is to:
- Aorta = Decrease systolic pressure, Increase diastolic pressure 3
- LV = Decrease systolic pressure, Decrease end diastolic pressure, Decrease Volume, Decrease Wall Tension 3
- Heart Overall = Decrease Afterload, Decrease Preload, Increase Cardiac Output 3
- Coronary Blood Flow = Increase 3
| Flashcard | type:basic |
|---|---|
| What is an IABP's overall broad brush physiological aims for the heart? | Increase Coronary Perfusion. Decrease the work the heart is up against (decreasing afterload) |
The balloon pump achieves this physiologically by:
- Coronary Blood Flow - Inflated balloon in diastole = Greater pressure during diastole = Greater amount of blood flowing back into coronary arteries = Improved coronary perfusion 3
- Afterload - Deflating balloon at point of systole = Lesser pressure for heart to beat against = Lesser workload for the heart = Lesser LV oxygen supply 3
What it does is:
- Reduce Afterload
- Increase Cardiac Output
- Optimise Coronary Flow
- Decreases Oxygen Consumption 1
Some mechanical complications of a balloon pump include:
Some other complications are:
- Loss of peripheral pulses 3
- Limb Ischaemia 3
- VTE 3
- Compartment Syndrome 3
- Aortic Dissection 3
- Vascular Injury 3
- Infection 3
- Balloon Rupture + Gas Embolus 3
- Baloon Entrapment 3
- Malpositioning = Renal/Cerebral Blood Flow Compromise 3
- Tamponade 3
| Flashcard | type:basic |
|---|---|
| An IABP is an intravascular decice, a balloon inflating and deflating in your aorta, so the complications it can cause are | All the problems you'd expect! Occlusion of blood flow to other places, damage to vasculature, and mechanical haemolysis! |
| What was the name of the main trial looking at IABP use for patients who had received PCI in cardiogenic shock? | IABP-SHOCK 2 |
| What did the IABP-SHOCK 2 Trial find? | In patients with cardiogenic shock who had received PCI, there was no difference in 30 day mortality between those who got a balloon pump and those who didn't. |
Patient needs to have a native beat and a stable rhythm. 1 Has been used for 40+ years. 1 Advantages are it's easy enough to insert, it's not too expensive, it doesn't have too many complications. Small cannula (7-8french) 1 But disadvantage is it only increases cardiac output by 500-800ml 1
Evidence around it:
IABP-SHOCK 2 Trial. 600 patients w/ cardiogenic shock who had been revascularised. Randomised to pump/no pump. No difference in 30 day mortality. 1
So now only recommended in the European Society Cardiology guidelines for when mechanical complications, rather than routinely. 1
Metaanalyses (Romeo) showed no advantage in short term or long term mortality when receiving IABP. 1
IABP does often get used as a bridge to other devices though. May have a role at supplementing other approaches, giving IABP with ECMO to reduce afterload. 1
[Acute Heart Failure]: